
US
°C
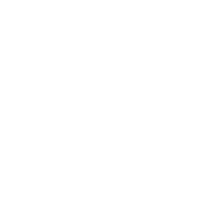



A bright blue glow captured off the waters off Sandbridge in Virginia Beach on Friday night, Aug. 14, 2015, caused by single-celled algae that are able to emit light.
(L. Todd Spencer/The Virginian-Pilot via AP)
Noctiluca scintillansarebright blue-green algae that createan ethereal blue glow to oceans around the world.While theirglow isremarkable at night, they are also indicators that fish die-offs are occurring.
Global warming isthe culprit behind recent growths of bioluminescent algae that are making the waters off India's coast glow bright blue but are alsokilling offfish, a new Indo-U.S. study says.
Noctiluca scintillans, also known as "sea sparkle," arebright blue-green algae that createan ethereal blue glow to oceans around the world, including recent reports near San Diego. While theirglow can draw crowds at night, they are also indicators that , according to a year-long study by NOAA and the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS).
“Less dense water comes to the surface because of the warming of oceans, encouraging these intense blooms, which has an adverse impact on fisheries. Currently, the western coast, Persian Gulfand Oman are largely affected, but if it keeps on increasing, it will have drastic effects on fisheries along the Indian coast. ,” S.C. Shenoi, director of INCOIS, told the Mint.
(MORE:)
In India, the phenomenon has been reportedalong Mumbai’sJuhu Beach. Previous studies indicated pollution was a contributingfactor for the blooms.
“Unfortunately, these beautiful patches indicate zones of decline because fish cannot thrive and sometimes die because of these blooms,” the study said.
The algae compete with fish for food and excrete large amounts of harmful ammonia.
The study notes that awarming climate will allow seawater layers to stratify more intensely, making it more difficult for nutrients to rise to the surface.
"Intensifying global-warming conditions may be expected to disrupt the fish-food chain and cause a decline of fisheries in the region,” the researchers said.







